What Planting Zone Is Wisconsin: A Comprehensive Guide To Understanding Wisconsin's Growing Zones
Wisconsin's planting zones play a crucial role in determining what plants thrive in the state's diverse climate. Whether you're a seasoned gardener or a novice looking to start your first garden, understanding Wisconsin's planting zones is essential for successful gardening. This guide will provide you with all the necessary information to help you make informed decisions about planting in Wisconsin.
Wisconsin is known for its vibrant landscapes, from lush forests to expansive farmlands. However, its climate varies significantly across different regions, affecting what can be grown and when. By understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map, you can identify which plants are best suited for your area and ensure they survive the state's harsh winters and variable summers.
This article will delve into the specifics of Wisconsin's planting zones, offering practical tips and expert advice for gardeners. Whether you're planting flowers, vegetables, or trees, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to succeed. Let's explore the world of gardening in Wisconsin and unlock its full potential.
- Ensure Price At Costco A Comprehensive Guide To Saving On Nutrition
- Unveiling The Mysteries Of The Zodiac The Sign For Aug 24
- Where Is Alex Oloughlin Now Latest Updates Amp Insights
- Uncovering The Origins Of Jelly Roll A Journey Through Music And Life
- Gucci Mane The Houston Texas Connection
Table of Contents
- Overview of Planting Zones in Wisconsin
- Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
- What Planting Zone is Wisconsin?
- How Climate Affects Wisconsin's Planting Zones
- Best Plants for Wisconsin's Planting Zones
- Seasonal Planting Guidance for Wisconsin
- Tips for Successful Gardening in Wisconsin
- Common Challenges in Wisconsin Gardening
- Useful Resources for Wisconsin Gardeners
- Conclusion: Thriving in Wisconsin's Planting Zones
Overview of Planting Zones in Wisconsin
Planting zones, also known as hardiness zones, are geographic areas defined by their average annual minimum winter temperatures. These zones help gardeners and farmers determine which plants are most likely to thrive in a specific location. Wisconsin spans several planting zones, each with its own unique characteristics and challenges.
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is the primary tool used to identify planting zones across the United States. In Wisconsin, the zones range from Zone 3b in the northernmost parts of the state to Zone 5b in the southern regions. This variation means that gardeners in different parts of Wisconsin may need to adjust their planting strategies accordingly.
Why Are Planting Zones Important?
Planting zones are critical for several reasons:
- Morgan Freeman The Voice Of A Generation
- Discover The Elegance Of The Harbor Breeze Lakeside Ceiling Fan
- 20 Heartwarming Diy Gift Ideas For Grandma That Shell Treasure Forever
- Exploring Flora Loca A Comprehensive Guide To This Unique Plant Phenomenon
- Spiderman 2 Full Cast Everything You Need To Know About The Iconic Superhero Movie
- They help determine which plants can survive the winter in a specific area.
- They provide guidance on when to plant and harvest crops.
- They assist in selecting plants that are best suited for local climate conditions.
Understanding the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map
The USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map is a valuable resource for gardeners and landscapers. It divides the United States into zones based on average annual minimum winter temperatures. Each zone represents a 10-degree Fahrenheit range, with subzones (a and b) representing 5-degree increments.
In Wisconsin, the map reveals a gradient of zones, with colder temperatures in the north and milder conditions in the south. This variation is due to factors such as elevation, proximity to large bodies of water, and prevailing weather patterns.
How to Use the USDA Map
To use the USDA Plant Hardiness Zone Map effectively:
- Locate your area on the map.
- Identify the corresponding zone and subzone.
- Select plants that are recommended for your specific zone.
What Planting Zone is Wisconsin?
Wisconsin's planting zones vary across the state, ranging from Zone 3b to Zone 5b. This diversity reflects the state's wide-ranging climate conditions. Northern Wisconsin, with its colder winters, falls into Zone 3b, while southern Wisconsin, with milder temperatures, is classified as Zone 5b.
Knowing your specific planting zone is essential for selecting plants that will thrive in your area. For example, Zone 3b gardeners may need to choose hardier plants that can withstand extreme cold, while Zone 5b gardeners can experiment with a wider variety of species.
Zone Breakdown in Wisconsin
- Zone 3b: Northernmost parts of Wisconsin, with average minimum temperatures of -35°F to -40°F.
- Zone 4a: Central and western regions, with average minimum temperatures of -30°F to -35°F.
- Zone 4b: Portions of central and southern Wisconsin, with average minimum temperatures of -25°F to -30°F.
- Zone 5a: Southern Wisconsin, with average minimum temperatures of -20°F to -25°F.
- Zone 5b: Southernmost parts of Wisconsin, with average minimum temperatures of -15°F to -20°F.
How Climate Affects Wisconsin's Planting Zones
Wisconsin's climate is characterized by cold winters and warm summers, with significant variations across the state. Factors such as temperature, precipitation, and soil conditions all influence the success of gardening efforts.
In northern Wisconsin, gardeners face challenges such as shorter growing seasons and harsh winters. In contrast, southern Wisconsin offers a longer growing season and milder temperatures, making it more suitable for a wider range of plants.
Key Climate Factors in Wisconsin
- Temperature: Average winter temperatures vary significantly across the state, affecting plant survival.
- Precipitation: Wisconsin receives ample rainfall, which benefits plant growth but can also lead to issues like waterlogging.
- Soil: The state's soil types range from sandy loam to clay, each requiring different planting strategies.
Best Plants for Wisconsin's Planting Zones
Choosing the right plants for your planting zone is crucial for success. In Wisconsin, gardeners have access to a wide variety of options, including flowers, vegetables, and trees. Here are some recommendations for each planting zone:
Zone 3b: Hardy Plants for Northern Wisconsin
- Flowers: Coneflowers, Black-eyed Susans, and Daylilies.
- Vegetables: Carrots, Potatoes, and Kale.
- Trees: Norway Spruce, Red Pine, and Quaking Aspen.
Zone 4a and 4b: Versatile Plants for Central Wisconsin
- Flowers: Lavender, Peonies, and Hostas.
- Vegetables: Tomatoes, Beans, and Cucumbers.
- Trees: Sugar Maple, Eastern White Pine, and Red Oak.
Zone 5a and 5b: Diverse Plants for Southern Wisconsin
- Flowers: Roses, Hydrangeas, and Tulips.
- Vegetables: Bell Peppers, Zucchini, and Sweet Corn.
- Trees: Redbud, Dogwood, and Birch.
Seasonal Planting Guidance for Wisconsin
Seasonal planting is an important consideration for Wisconsin gardeners. The state's climate dictates specific planting and harvesting times for various crops. Here's a guide to help you plan your garden throughout the year:
Spring Planting
In spring, focus on planting cool-season crops like lettuce, spinach, and radishes. This is also a good time to start seeds indoors for warm-season crops like tomatoes and peppers.
Summer Planting
During the summer, plant warm-season vegetables such as cucumbers, squash, and beans. Be sure to water regularly and mulch to retain soil moisture.
Fall Planting
Fall is an ideal time to plant bulbs for spring blooms, as well as cool-season crops like broccoli and cauliflower. This is also a good opportunity to prepare your garden for winter.
Tips for Successful Gardening in Wisconsin
To ensure success in your Wisconsin garden, consider the following tips:
- Test your soil regularly to determine its nutrient levels and pH.
- Choose plants that are well-suited to your specific planting zone.
- Use mulch to conserve moisture and suppress weeds.
- Practice crop rotation to prevent soil depletion and pest buildup.
- Protect plants from extreme weather conditions using row covers or other methods.
Common Challenges in Wisconsin Gardening
Gardening in Wisconsin comes with its own set of challenges. Here are some common issues and how to address them:
Dealing with Frost
Frost is a significant concern for Wisconsin gardeners, especially in early spring and late fall. To protect your plants from frost damage, cover them with frost blankets or move potted plants indoors.
Pest Management
Pests such as deer, rabbits, and insects can wreak havoc on gardens. Use physical barriers, repellents, and natural predators to manage pest populations effectively.
Soil Issues
Wisconsin's diverse soil types can pose challenges for gardeners. Amend your soil with organic matter to improve its structure and fertility.
Useful Resources for Wisconsin Gardeners
Here are some valuable resources to help you succeed in gardening in Wisconsin:
Conclusion: Thriving in Wisconsin's Planting Zones
Understanding what planting zone is Wisconsin and how it affects gardening is essential for success. By selecting plants that are well-suited to your specific zone and following best practices for planting and care, you can create a thriving garden that withstands the state's variable climate.
We encourage you to take action by experimenting with different plants and techniques in your garden. Share your experiences and insights with fellow gardeners, and don't hesitate to explore other resources and articles on our site for more information. Happy gardening!
- Selena Gomez Hand Cream The Ultimate Guide To Soft Hydrated Hands
- Exploring The Expanding Universe Of Yellowstone What Are All The Yellowstone Spin Offs
- Anos Voldigoad Pfp A Comprehensive Guide To The Iconic Profile Picture
- Matthew Mcconaughey The Journey Of A Versatile Hollywood Icon
- Unraveling The Mystery What Age Did Priscilla Leave Elvis

23+ Wisconsin Planting Zone Map AlyshaPatrekur
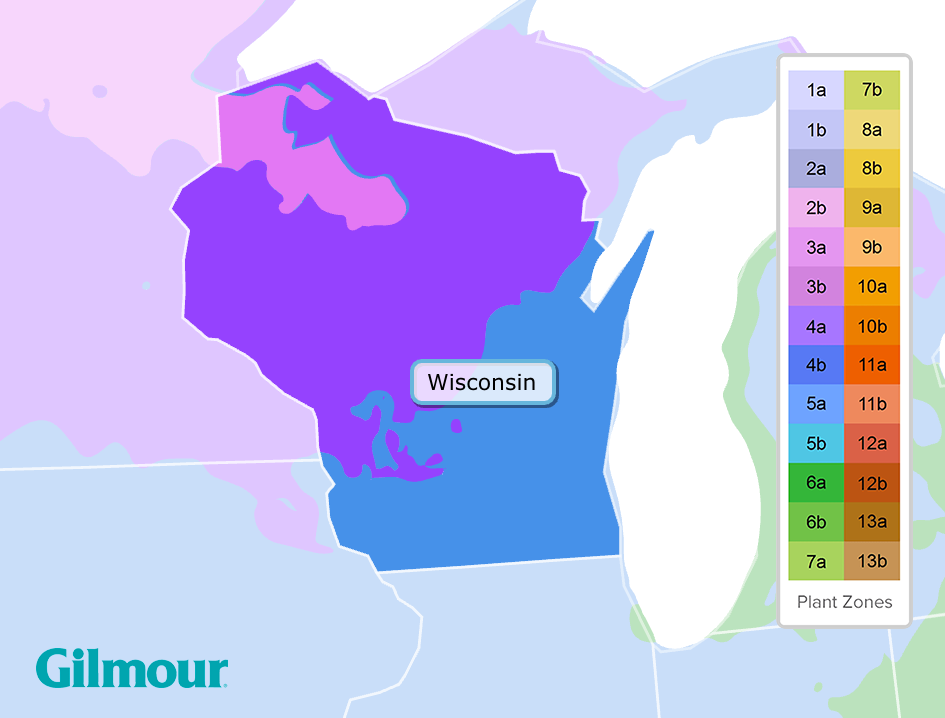
Wisconsin Planting Zones Growing Zone Map Gilmour
What Planting Zone Is Wisconsin PlantopiaHub Your Ultimate